-
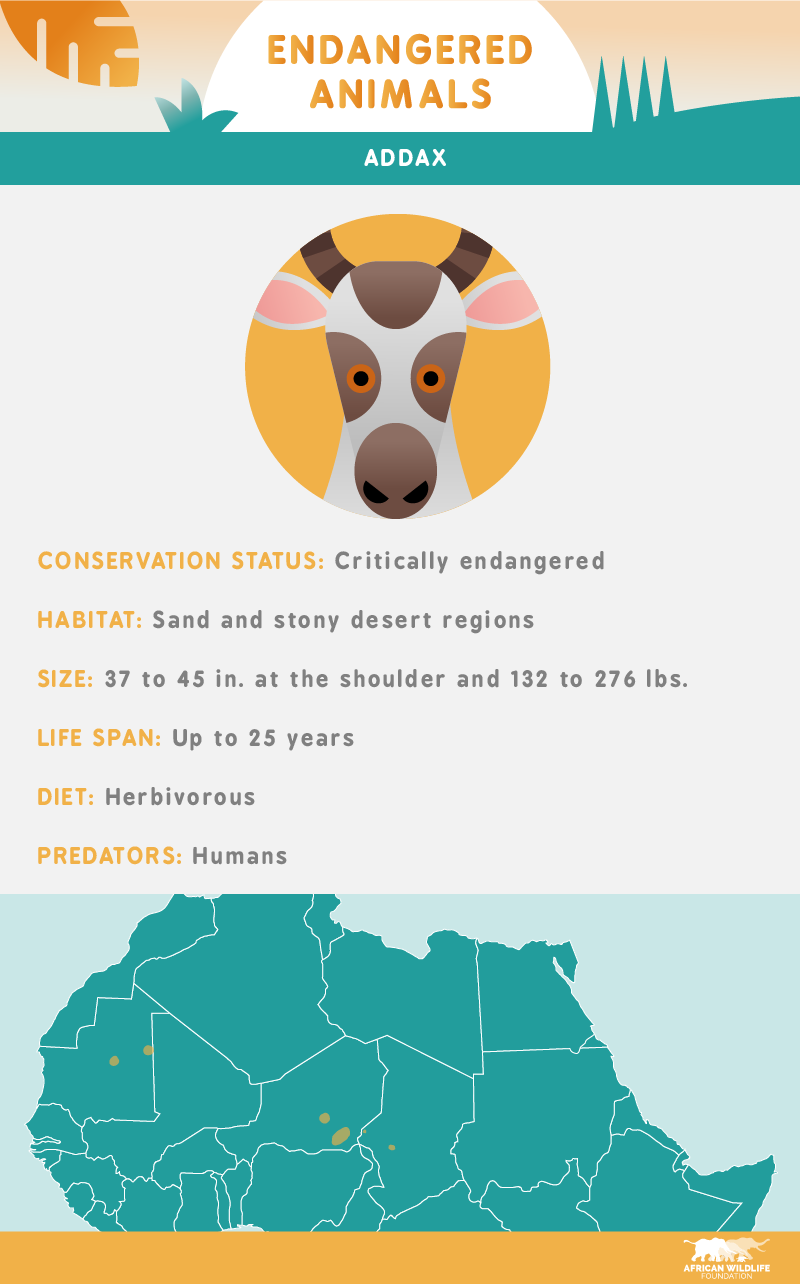
Like many African animals, the greatest threat the critically endangered addax faces is humans. As a result of overhunting, there may be less than 100 addax remaining in the wild today.
-
One of the animals closest to humans in its genetic makeup, the African chimpanzee is considered endangered today, with a population of less than 300,000 remaining in the wild. Despite their large community sizes (up to 150 individual chimps), one of the primary threats to the survival of the African chimpanzee is disease, deforestation, and hunting.
-
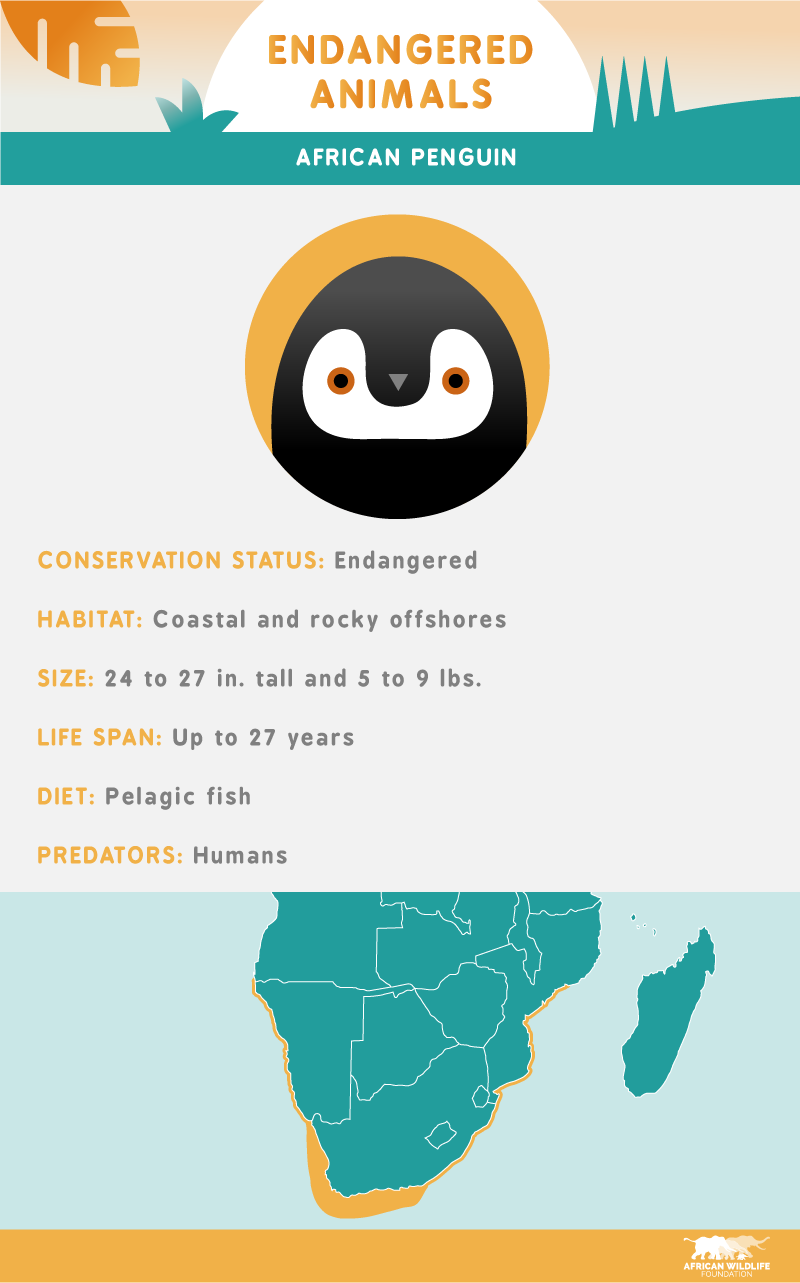
You may not expect to find penguins in Africa, but the African penguin is the only species of penguin found exclusively in Africa. As a result of the destruction of its habitat and the harvesting of its eggs for food, the African penguin is identified as endangered today.
-
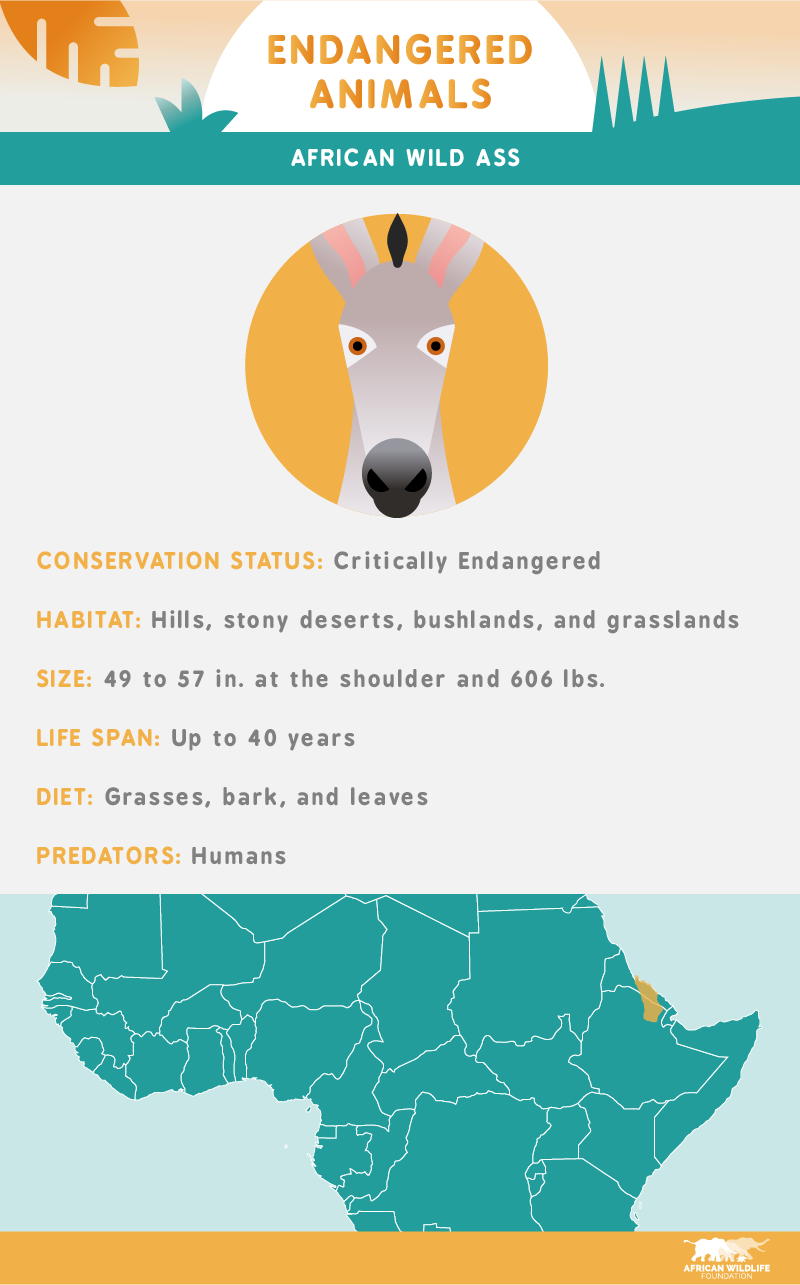
The African wild ass, another critically endangered species in Africa, has as many as 600 individuals left in the wild; however, the exact figures are hard to determine between the two major countries this animal is native to. The African wild ass is currently in danger of extinction due to hunting for medicinal and food purposes.
-
Many farmers shoot or poison the African wild dog, which is often blamed when leopards or hyenas kill their livestock, leading to their status as an endangered species. Once bountiful across many African regions, today approximately 6,600 remain in the wild.
-
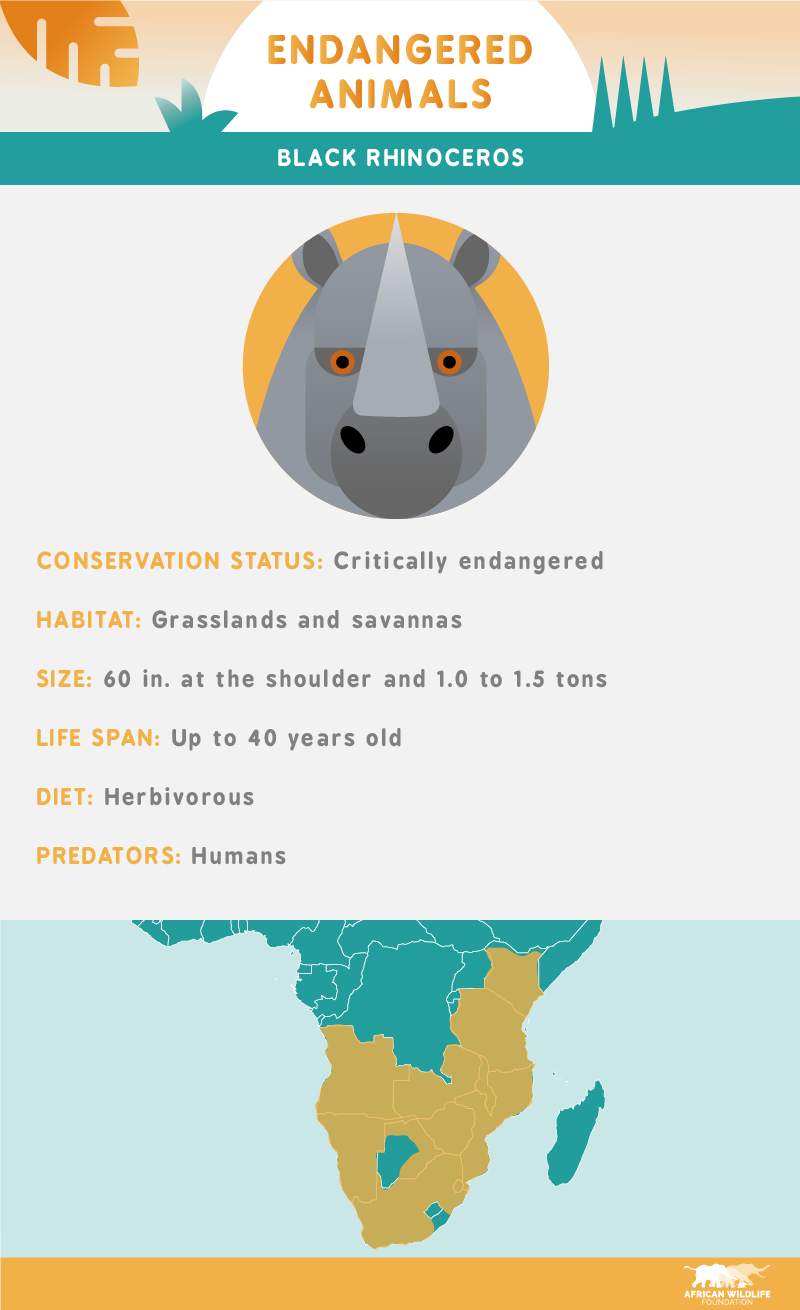
Today, the black rhinoceros population is down by nearly 98 percent since 1960. Despite its rapidly declining numbers, the black rhino has no predators except for humans. Roughly 40 percent of the world’s remaining black rhinos (considered critically endangered) live in South Africa.
-
There are currently 11 species of vulture in Africa, including the Cape vulture, which is currently listed as endangered. Found in the mountainous regions of Africa, poachers are among the primary threats to the Cape vulture today. Because vultures flock to the sites of dead animals, poachers have turned to killing vultures to help remain undetected.
-
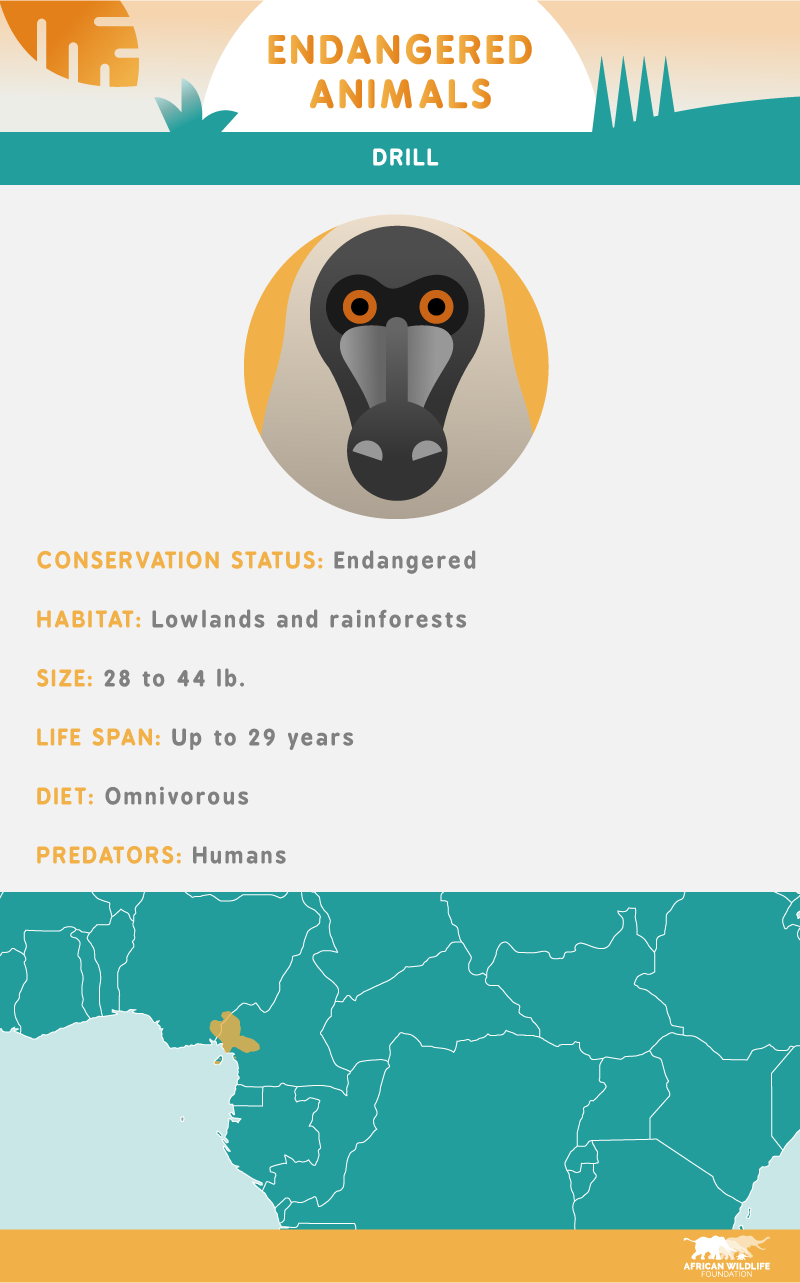
Because the drill occupies a relatively small space in Africa, habitat loss is currently the most prevalent threat to this endangered species. Some are also captured for captivity, killed for their meat, or killed by farmers defending their crops.
-
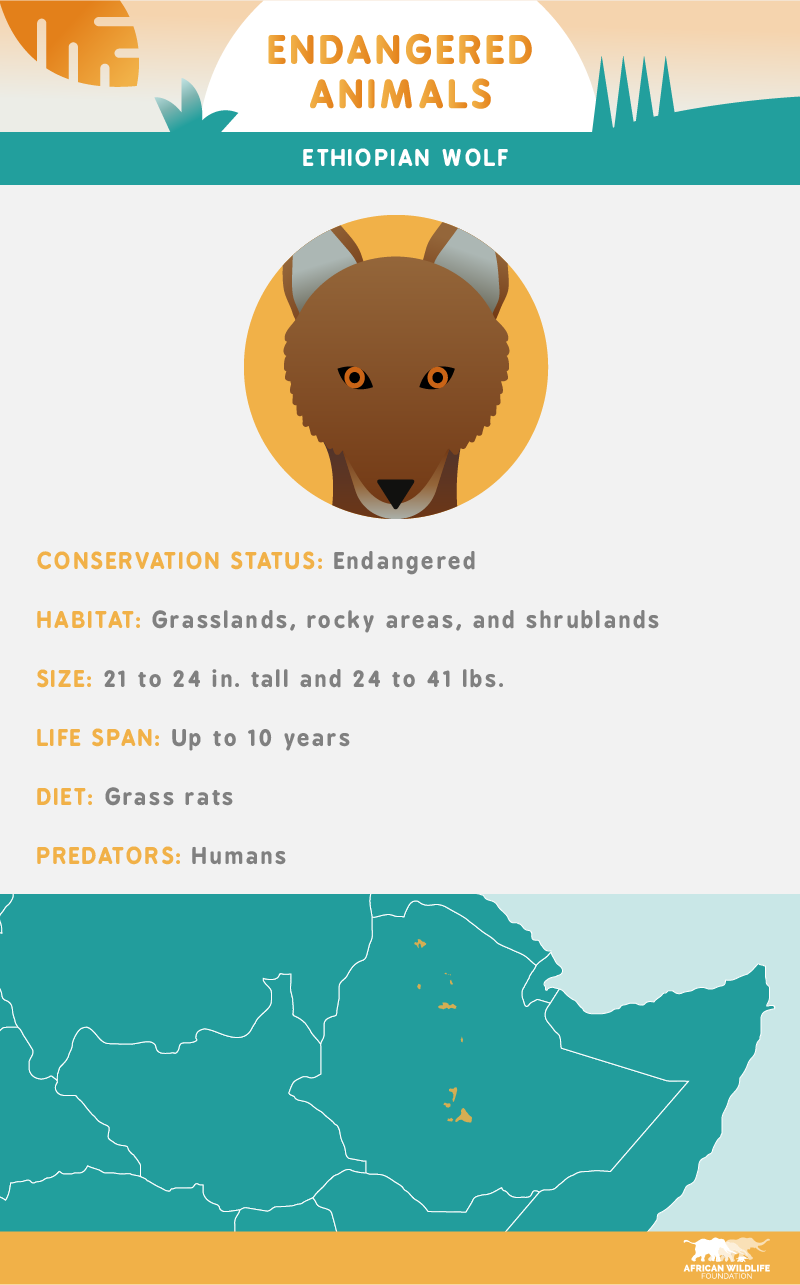
The Ethiopian wolf is found only in Ethiopia with fewer than 600 adults remaining in the wild, making it one of Africa’s most endangered species. Subsistence farming in Ethiopia and the overgrazing of livestock are currently among the most critical challenges facing the Ethiopian wolf in addition to disease and outbreaks.
-
The Grevy’s zebra is often hunted for its striking skin and is considered endangered today, with approximately 2,000 mature individuals remaining in the wild. Over the last three decades, the Grevy’s zebra has seen a population decline of about 50 percent.
-
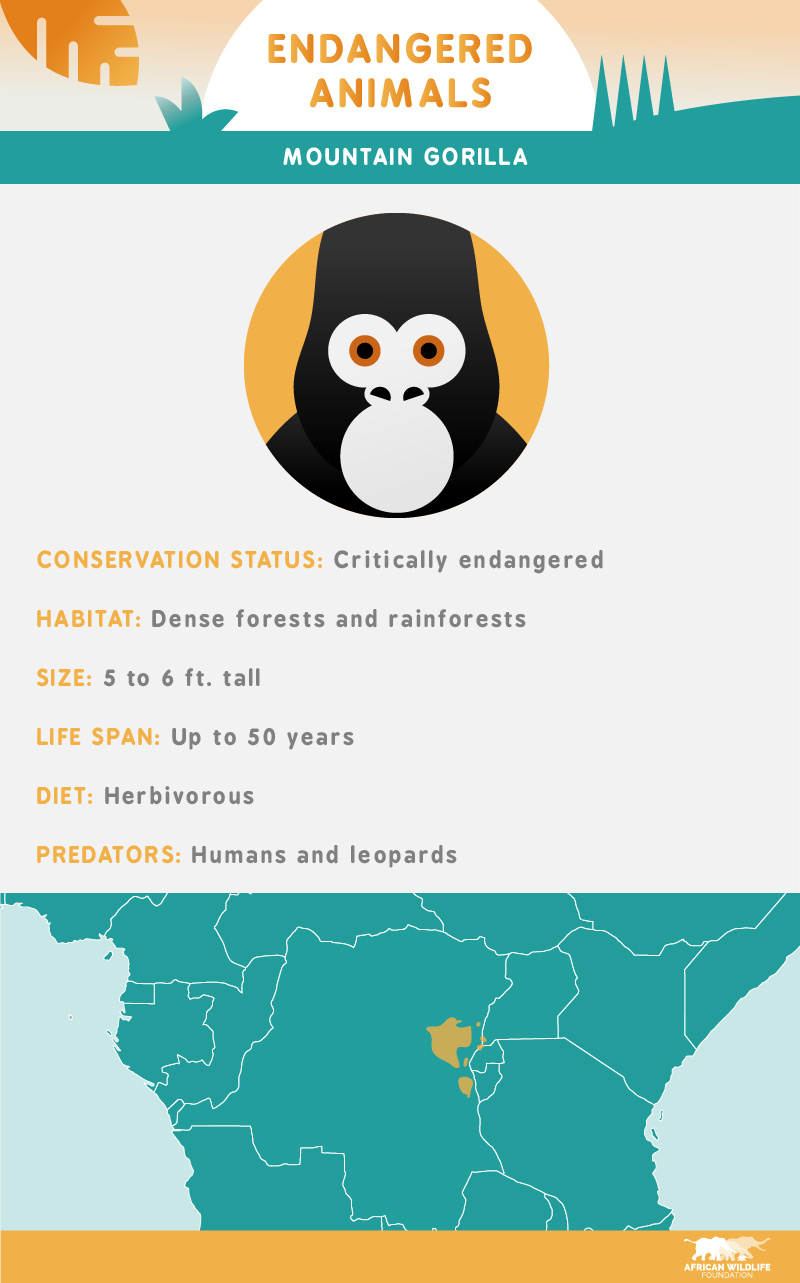
Mountain gorillas are the largest living primates in the world and remain critically endangered. Despite their average life span of 40 to 50 years, less than 1,000 mountain gorillas exist today, and they can only be found in four national parks in three African countries.
-
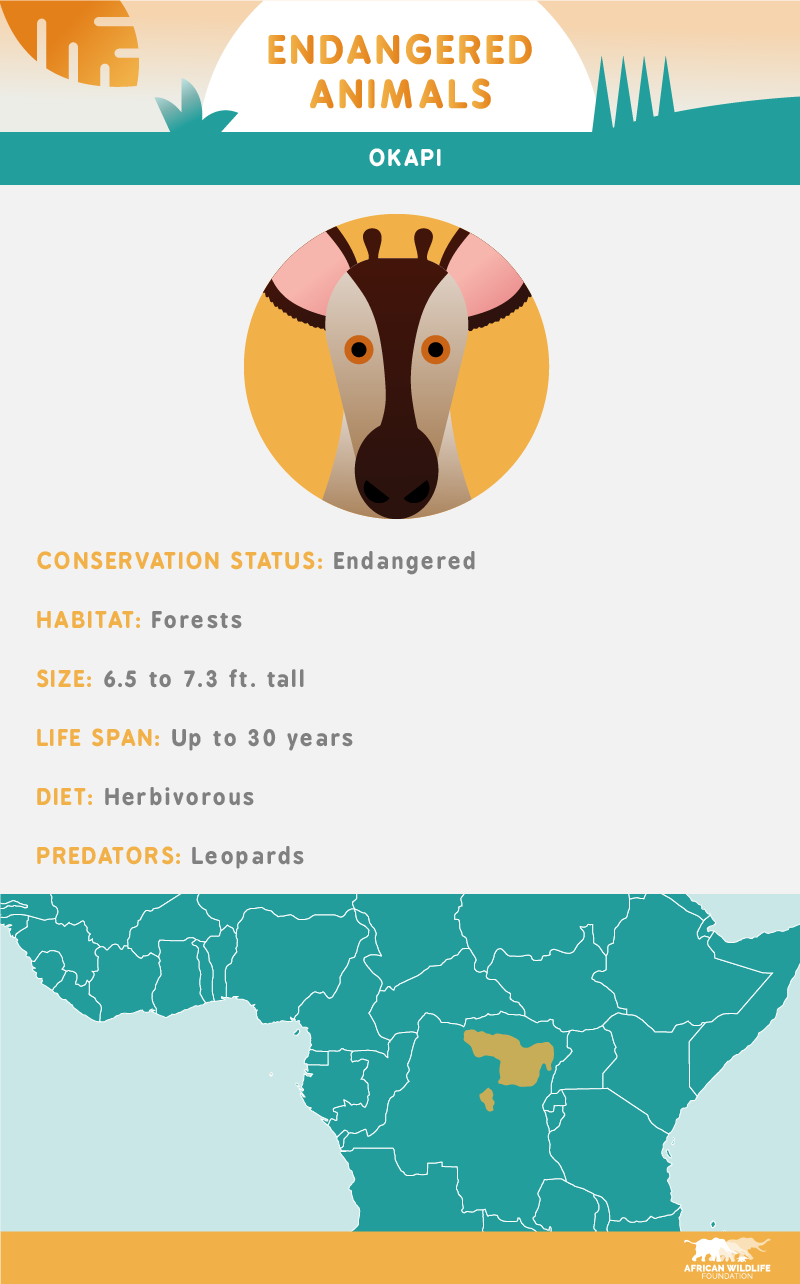
Today, the okapi population is declining at a rapid rate and is considered endangered. The primary concern for okapi in the wild is habitat loss in areas of active settlement.
-
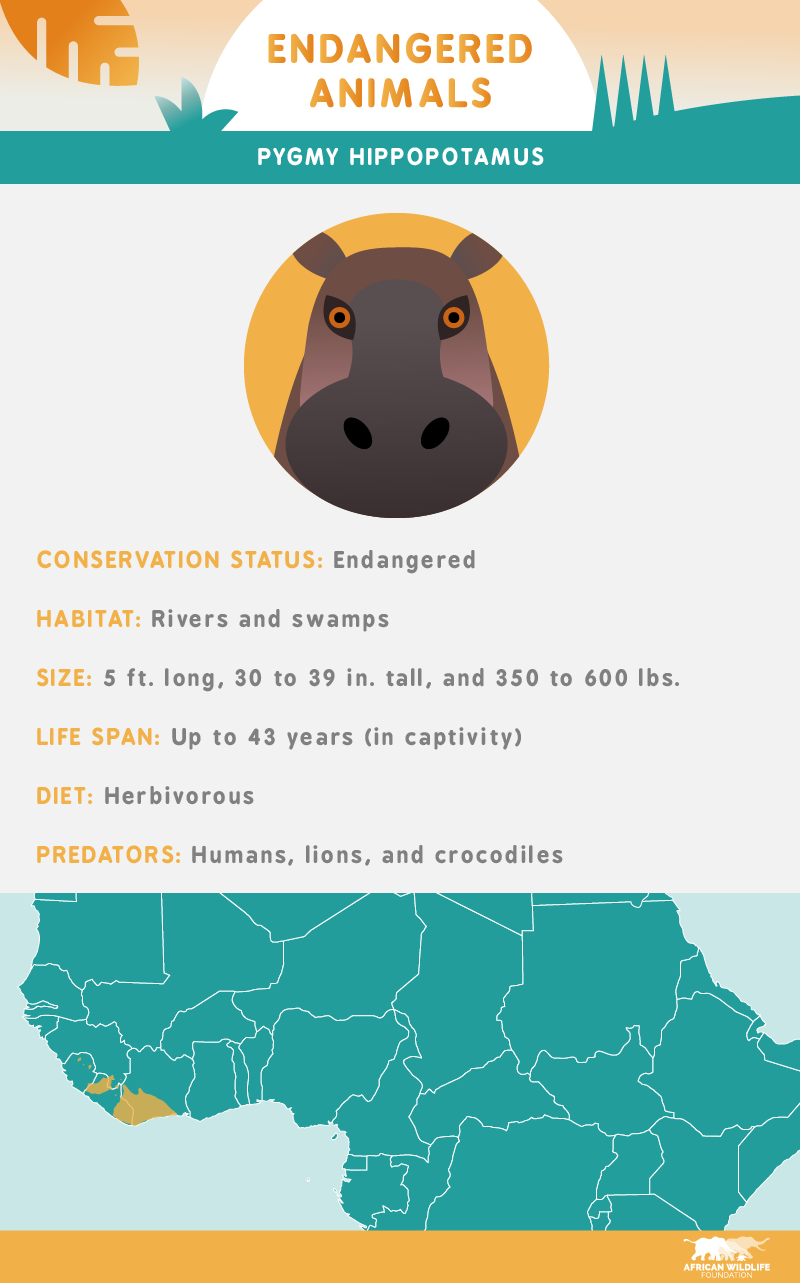
The pygmy hippopotamus – listed as endangered – is the smaller of the two hippo breeds and is considered a shy forest dweller. Confined to very restricted ranges in West Africa, the pygmy hippopotamus is now considered rare in the wild.
-
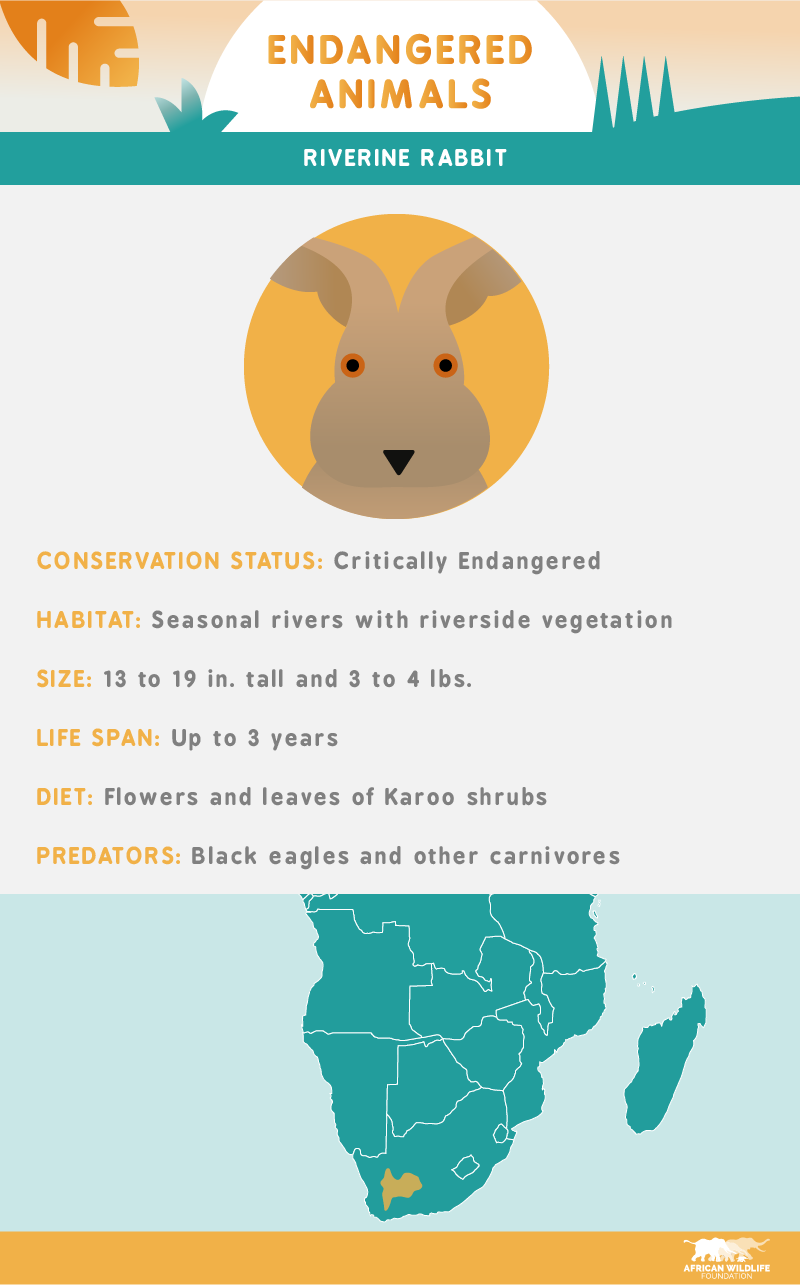
The riverine rabbit, a critically endangered species found near African rivers and riverside vegetation, has no more than 50 individuals in any subpopulation. With a declining population, the biggest threats to the riverine rabbit are land degradation and habitat loss due to farming and hunting.
-
Today, the Rondo Bushbaby is among the most critically endangered species in the world. Found in only seven highly threatened forest patches throughout Africa, the exact number of Rondo Bushbaby animals left in existence is unknown but under severe threat, severely fragmented, and continues to experience decline.